Gene & Genetic engineering
■ Genes & Genetic Engineering :
● What are Genes ?
------) Genes are the functional units of DNA .
• They represents various traits of an organism represented by base pair sequences in DNA.
• Every aspect of that human being is represented by genes. For eg- Skin colour, Hair colour are represented by particular sequence of base pairs in any organism.
■ Genetic Engineering-----) Term coined by Jack Williamson in his science fiction novel Dragon's Island, published in 1951.
• Is the core technique of Biotechnology .
• It involves the process of alteration of genes or to alter chemistry of genetic material to produce a desired trait. Father of Genetic Engineering Paul Berg .
• Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen (both American Scientists)were pioneers of recombinant DNA (r DNA) technology which made basis for the Biotechnology.
■ Recombinant DNA Technology: Recombinant DNA or r DNA is a unique DNA strand which is created artificially by joining two or more strands which behaves like naturally occurring DNA.
• Modern Biotechnology has been possible because of this process.
• With this technology, a gene or multiple genes can be identified, cut, and inserted into the genome of another organism.
■ Tools used in r DNA Technology:
---1. Restriction Enzymes: -Discovered by Herbert Boyer and their purpose is to cut the DNA at specific locations (specific recognition sequence) -Two types: Endonucleases(cut at specific location) and Exonucleases(cut at terminal location)
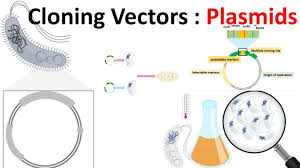
2. Cloning vectors: -Certain molecules in bacteria such as plasmids and Bacteriophages have ability to replicate themselves without the control of
chromosomal DNA -Cloning vector is chosen according to size and type of DNA to be cloned.
3. Competent Host: -To prepare the host cell take up the rDNA done by micro injection or Gene gun (biolistics).
■ Recombinant DNA Technology (contd.)
• Process of r DNA Technology :
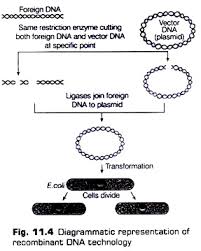
1.Isolation of DNAs - In this step we extract pure DNAs - Hence we need to open the cell and extract the DNA - With the help of enzymes such as lysozyme (bacteria), cellulase (plant cells), chitinase (fungus).
2. Cutting the DNA at specific location - We use restriction enzymes which cut the DNA at specific location for source as well as vector DNA - Agarose gel electrophoresis is used to check the progression of restriction endonucleases - Both the fragmented DNAs are mixed with ligases resulting in the formation of r DNA..
3. Amplification of Gene of interest - For this we use PCR Technique (Polymerase Chain Reaction) - It was identified by US Bio Chemist K B Mullis in 1983 - It is used to make multiple copies of DNA or gene - In this we use thermostable DNA polymerase (isolated from Bacterium Thermus aquaticus)
4. Insertion of r DNA into the Host Cell/Organism - In this step we insert the recombinant DNA into the host cell - For this we provide anti medium to cell in which only recombinant cell can grow and other cell will die using selectable marker.-Eg: If r DNA resistant to ampilicin(antibiotic) is transformed into host e coli cell then its cell is transformed into ampicillin-resistant cells. If we spread the transformed cell into a medium containing ampilicin then only ampicilin resistant cell (act as selectable marker) will grow and others will die.
5. Obtaining the foreign gene product -In this step we produce the desired product for which we have made the r DNA (basically proteins) using Bio Reactors - Bio Reactors is a large volume of culture having raw material and optimum conditions to create the desired product like proteins, enzymes, antibodies etc. on large scale .
6. Downstreaming Process Includes the process of separation and purification of the required product from Bioreactors which is collectively known as Downstreaming process. The finished product has to be tested in laboratory before it is released. Human insulin production.
● What are Genes ?
------) Genes are the functional units of DNA .
• They represents various traits of an organism represented by base pair sequences in DNA.
• Every aspect of that human being is represented by genes. For eg- Skin colour, Hair colour are represented by particular sequence of base pairs in any organism.
■ Genetic Engineering-----) Term coined by Jack Williamson in his science fiction novel Dragon's Island, published in 1951.
• Is the core technique of Biotechnology .
• It involves the process of alteration of genes or to alter chemistry of genetic material to produce a desired trait. Father of Genetic Engineering Paul Berg .
• Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen (both American Scientists)were pioneers of recombinant DNA (r DNA) technology which made basis for the Biotechnology.
■ Recombinant DNA Technology: Recombinant DNA or r DNA is a unique DNA strand which is created artificially by joining two or more strands which behaves like naturally occurring DNA.
• Modern Biotechnology has been possible because of this process.
• With this technology, a gene or multiple genes can be identified, cut, and inserted into the genome of another organism.
■ Tools used in r DNA Technology:
---1. Restriction Enzymes: -Discovered by Herbert Boyer and their purpose is to cut the DNA at specific locations (specific recognition sequence) -Two types: Endonucleases(cut at specific location) and Exonucleases(cut at terminal location)
2. Cloning vectors: -Certain molecules in bacteria such as plasmids and Bacteriophages have ability to replicate themselves without the control of
chromosomal DNA -Cloning vector is chosen according to size and type of DNA to be cloned.
3. Competent Host: -To prepare the host cell take up the rDNA done by micro injection or Gene gun (biolistics).
■ Recombinant DNA Technology (contd.)
• Process of r DNA Technology :
1.Isolation of DNAs - In this step we extract pure DNAs - Hence we need to open the cell and extract the DNA - With the help of enzymes such as lysozyme (bacteria), cellulase (plant cells), chitinase (fungus).
2. Cutting the DNA at specific location - We use restriction enzymes which cut the DNA at specific location for source as well as vector DNA - Agarose gel electrophoresis is used to check the progression of restriction endonucleases - Both the fragmented DNAs are mixed with ligases resulting in the formation of r DNA..
3. Amplification of Gene of interest - For this we use PCR Technique (Polymerase Chain Reaction) - It was identified by US Bio Chemist K B Mullis in 1983 - It is used to make multiple copies of DNA or gene - In this we use thermostable DNA polymerase (isolated from Bacterium Thermus aquaticus)
4. Insertion of r DNA into the Host Cell/Organism - In this step we insert the recombinant DNA into the host cell - For this we provide anti medium to cell in which only recombinant cell can grow and other cell will die using selectable marker.-Eg: If r DNA resistant to ampilicin(antibiotic) is transformed into host e coli cell then its cell is transformed into ampicillin-resistant cells. If we spread the transformed cell into a medium containing ampilicin then only ampicilin resistant cell (act as selectable marker) will grow and others will die.
5. Obtaining the foreign gene product -In this step we produce the desired product for which we have made the r DNA (basically proteins) using Bio Reactors - Bio Reactors is a large volume of culture having raw material and optimum conditions to create the desired product like proteins, enzymes, antibodies etc. on large scale .
6. Downstreaming Process Includes the process of separation and purification of the required product from Bioreactors which is collectively known as Downstreaming process. The finished product has to be tested in laboratory before it is released. Human insulin production.







Comments
Post a Comment